Year 2024 started with high hopes on economic recovery. Inflation seemed to be contained, and rate cuts were on horizon.
Months later, the hope is fading away. Now, there is more pessimism than optimism.
Inflation Risk
Strong jobs data, coupled with geopolitical risk, are keeping the inflation at top range target of 2,5+1% (i.e. 3,05% YoY in March 2024).
If this persists, more households may start chewing their own savings. Even as the younger generations save more, they are less incline to invest compared to the older generations. This is concerning, as their purchasing power reduces along with inflation.
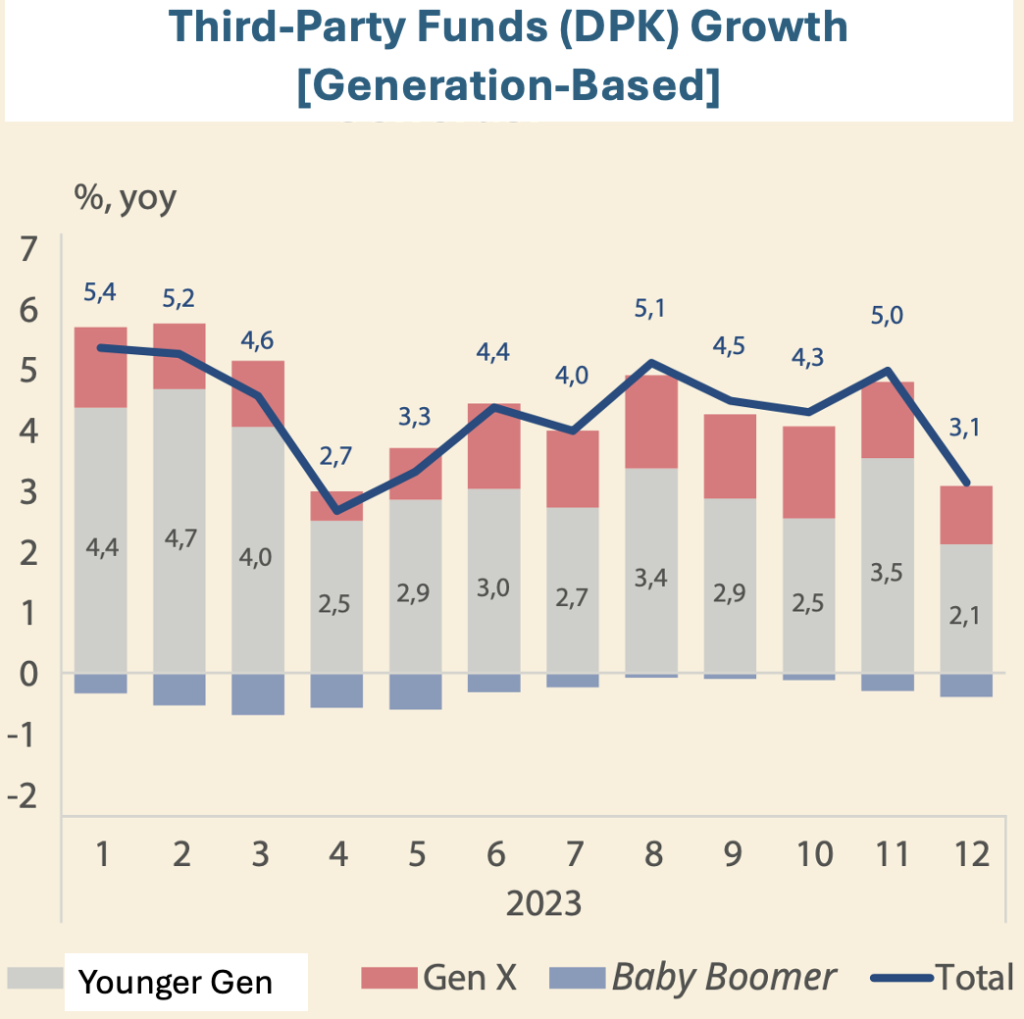
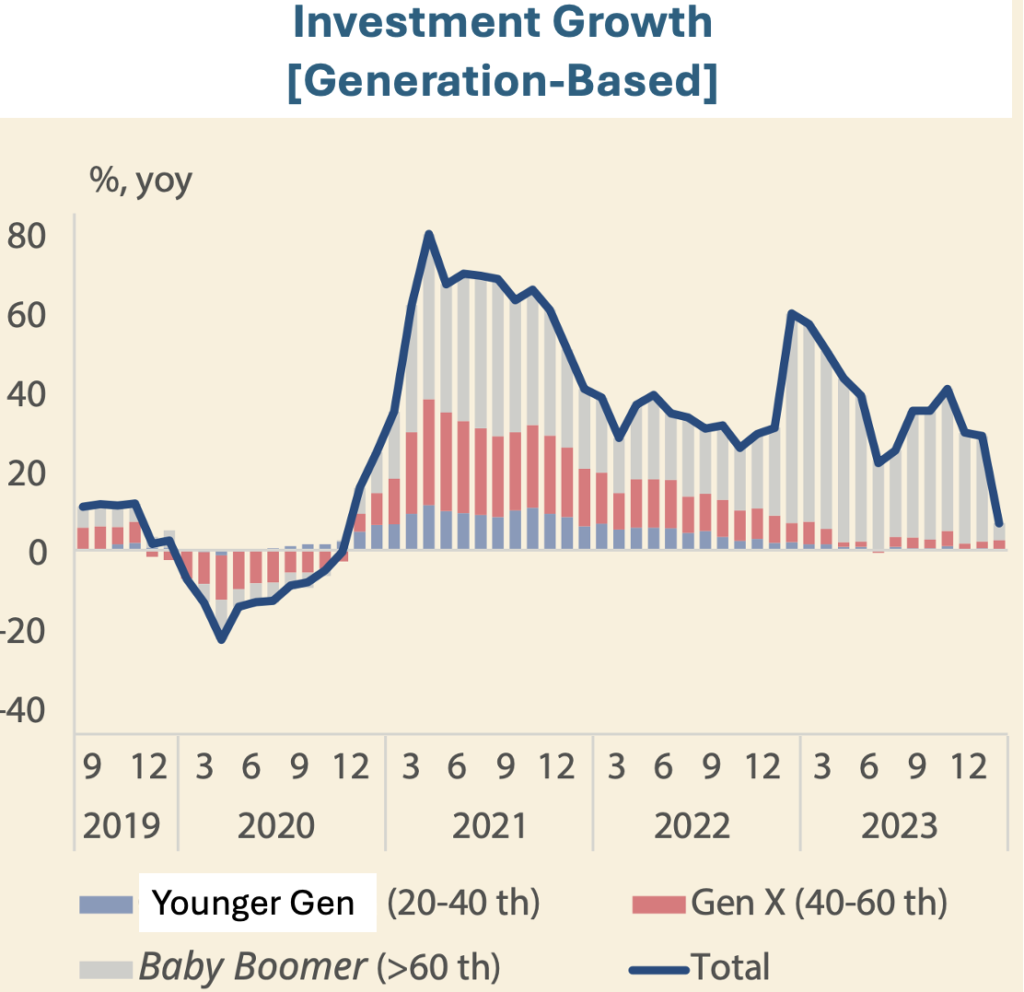
Higher Rates for Longer
The Fed recently indicated that higher rates might stay longer than previously expected.
As for the country, the Central Bank [24th April 2024] had decided to hike the interest rate by another 25 bps to 6,25%.
It is a pre-emptive move; despite the Fed’s rate being on hold. The IMF itself suggested that the Asian Central Banks shouldn’t be too dependent on the Fed’s movement in their decision-making process.

Currency Depreciation
Capital flights have resulted in weaker currencies for most developing countries, including the neighbouring South East Asian countries.
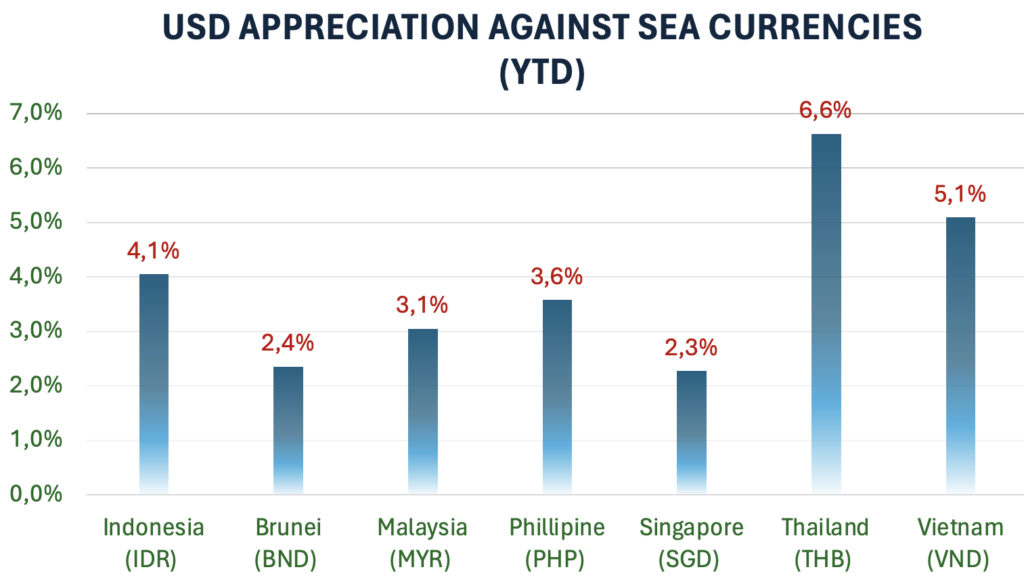
Apart from hiking the rates, the Foreign Exchange Reserve can be used to intervene the slide. However, it can not be exhausted to solely defend the currency. Bear in mind, the Reserve serves other purpose as well.

GDP Impact
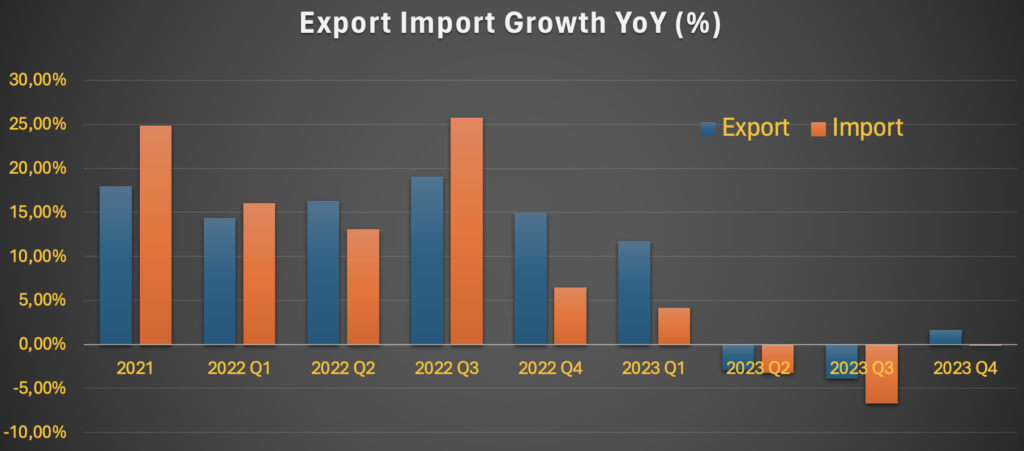
Owing to the government stimulus and spending since the pandemic, the GDP has performed relatively well so far (i.e. 5,11% YoY in Q1 2024).
However, should the geopolitical situation escalate, the impact from cross-border trade might hit the GDP. Year 2023 itself had witnessed a flattening growth.
What Could Happen Next
Inflation
Consumer price inflation may eventually drive up the wage growth, which in turn will drive the price inflation higher for months or years.
Rate Movement
The Central Bank would be left with little option between raising it again or holding on as long as it can. Although, another rate increase might hurt the economy at a moment when it needs stimulus instead.
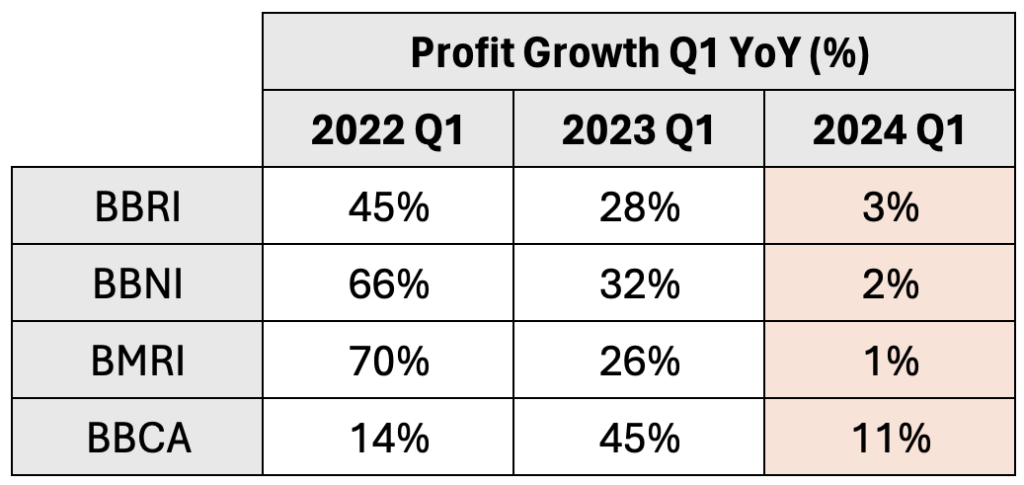
Banks
To maintain credit growth, banks may be forced to trim their NIM (Net Interest Margins). Subsequently, it could adversely impact their profit growth. The latest Q1 2024 financial results showed a decline in their profit growths, barely keeping up with inflation rate.
This is a defining moment in which the economy is being tested on how resilient it can be against all odds.
Disclaimer: NOT FINANCIAL / INVESTMENT ADVICE. This article is of writer’s personal opinion. Any information contained here is for education and informational purpose only. Readers should seek other sources or professional advice for further clarification where deemed necessary.

